CBSE Class 10 Math Sample Paper 2019
Video Solutions | 4 Mark Questions | Section D | 8 Questions
Section D contains 8 questions of 4 marks each. Scroll down for explanatory answer and video solution to the 4-mark questions that appeared in Class 10 Maths CBSE board exam in 2019. Questions appeared from the following chapter : Quadratic Equations, Arithmetic Progressions, Triangles, Trigonometry, Surface Areas & Volumes, Applications of Trigonometry, and Statistics.
Question 23 | Internal Choice A
A train takes 2 hours less for a journey of 300 km if its speed is increased by 5 km/h from its usual speed. Find the usual speed of the train.
How to solve this Quadratic Equations word problem?
Step 1: Assign a variable for the usual speed of the train.
Step 2: Frame an equation each for time taken to cover 300 km at s km/hr and (s + 5) km/hr respectively.
Step 3: Simplify the two equations to get a quadratic equation in 's'.
Step 4: Solve for s to arrive at the answer.
ORQuestion 23 | Internal Choice B
Solve for x: \\frac{1}{(a + b + x)}) = \\frac{1}{a}) + \\frac{1}{b}) + \\frac{1}{x}) , [a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0, x ≠ 0, x ≠ -(a + b)]
Approach to solve this Quadratic Equations problem
Step 1: Take LCM of denominators on both sides of the equation.
Step 2: Cross multiply to get a quadratic equation in x.
Step 3: Factorize the quadratic equation to find two answers for x.
Question 24
An AP consists of 50 terms of which 3rd term is 12 and the last term is 106. Find the 29th term.
How to solve this Arithmetic Progressions question?
Concept: The formula to find the nth term of an AP is an = a + (n - 1)d, where a is the first term, n is the number of terms, and d is the common difference of the AP.
Step 1: Express the third term in terms of the first term of the AP and the common difference. Call it equation (1).
Step 2: Express the 50th term in terms of the first term and the common difference. Call it equation (2).
Step 3: Solve equations (1) and (2) to find the value of d.
Step 4: Substitute the value of 'd' in one of the two equations to find 'a'.
Step 5: Compute the value of the 29th term using the values of a and d computed in steps 3 and 4.
Question 25
Prove that in a right angled triangle square of the hypotenuse is equal to sum of the squares of other two sides.
Hint to solve this Triangles problem
Concept: Proving the Pythagoras Theorem.
Theorem: If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse then triangles on both sides of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other.
Step 3: Draw a right triangle ABC right angled at B. Draw BD ⊥ AC
Step 4: From the theorem, ΔADB ~ ΔABC and ΔBDC ∼ ΔABC (Theorem)
Step 5: Therefore, \\frac{AD}{AB}) = \\frac{AB}{AC}) and \\frac{CD}{BC}) = \\frac{BC}{AC})
Step 6: Solve the above equations and add them to prove Pythagoras Theorem.
Question 27 | Internal Choice A
A man on the top of a vertical observation tower observes a car moving at a uniform speed coming directly towards it. If it takes 12 minutes for the angle of depression to change from 30° to 45°, how long will the car take to reach the observation tower from this point?
Hint to solve this Applications of Trigonometry problem
![Applications of Trigonometry Q27A]()
Step 1: Apply tan 45 in triangle ACD and establish that CD = AD.
Step 2: Apply tan 30 in triangle ABD and compute BC in terms of CD.
Step 3: It takes 12 seconds to cover BC. So, compute time taken to cover CD.ORQuestion 27 | Internal Choice B
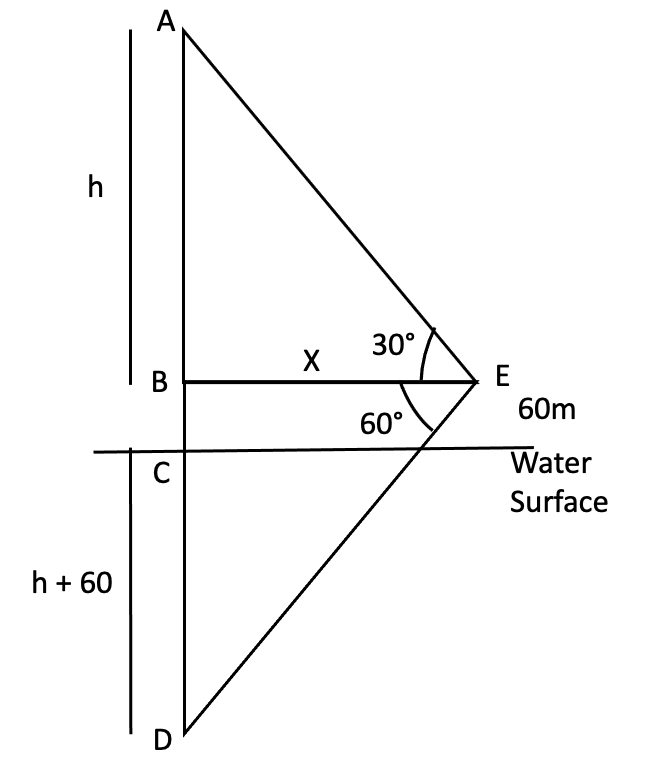
The angle of elevation of a cloud from a point 60 m above the surface of the water of a lake is 30° and the angle of depression of its shadow from the same point in water of lake is 60°. Find the height of the cloud from the surface of water.
Approach to prove Applications of Trigonometry problem
![Applications of Trigonometry Q27B]() Step 1: In triangle ABE, find tan of angle of elevation and express BE in terms of height of the cloud.
Step 1: In triangle ABE, find tan of angle of elevation and express BE in terms of height of the cloud.
Step 2: In triangle BDE, compute tan 60 and compute h after substituting BE in terms of h.
Question 28 | Internal Choice A
The median of the following data is 525. Find the values of x and y if the total frequency is 100.
Class Interval Frequency Class Interval Frequency 0-100 2 500-600 20 100-200 5 600-700 y 200-300 x 700 – 800 9 300-400 12 800-900 7 400-500 17 900-1000 4 Hint to solve this Statistics problem
Step 1: Identify the median class and substitute values in the median formula for grouped data.
Step 2: Solve the equation by substituting median as 525 and compute value for x.
Step 3: Substitute value of x and compute value of y.ORThe following data indicates the marks of 53 students in Mathematics. Draw less than type ogive for the data and hence find the median.
Marks No.of.students Marks No.of.students 0-10 5 50-60 4 10-20 3 60-70 7 20-30 4 70 – 80 9 30-40 3 80-90 7 40-50 4 90-100 8 Approach to solve this Statistics problem
Step 1: Compute cumulative frequency table from grouped data for less than the upper limit of each class interval.
Step 2: Draw the less than type ogive with the upper limit as the x-axis and the cumulative frequency as the y-axis.
Step 3: Drop a perpendicular at the point where the cumulative frequency is 27 (54/2) and find the value on the x-axis where the perpendicular meets the x-axis to compute the median.
Question 29
The radii of the circular ends of a bucket of height 24 cm are 15 cm and 5 cm. Find the area of its curved surface.
Hint to solve this Surface Areas problem
Formulae Used: CSA of frustum of cone = π × (R + r) × l, where R and r are the radii of the top and bottom of the frustum of the cone and l is the slant height.
Step 1: Compute slant height using Pythagoras Theorem.
Step 2: Compute CSA of frustum of cone using the radii of the top and bottom of the bucket and the slant height computed in step 1.
Question 30
If sec θ + tan θ = p, then find the value of cosec θ.
Hint to solve this Trigonometry problem
Step 1: Rewrite sec θ and tan θ in terms of sin θ and cos θ
Step 2: Express cos θ = \\sqrt{1 – {sin}^{2}θ})
Step 3: Square both sides of the equation. Will result in a quadratic equation with sin θ being the variable.
Step 4: Solve the quadratic equation for sin θ using the quadratic formula.
Step 5: The reciprocal of the values obtained for sin θ are the answers to the question asked.
Try CBSE Online Coaching
Class 10 Maths
Register in 2 easy steps and
Start learning in 5 minutes!
FREE Online Revision Classes
CBSE Class 10 Maths - 2021
- Real Numbers Revision Class
- Polynomials Revision Videos
- Linear Equations Revision Class
- Quadratic Equations Revision Class
- Arithmetic Progressions Revision Video
- Triangles Revision
- Coordinate Geometry Revision
- Trigonometry Revision Class
- Appl of Trigonometry
- Circles Revision Class
- Areas Related to Circles Revision Videos
CBSE Online Coaching | Sample Question Paper Class 10 Maths 2019 Video Solution
1. Section A | 2018 CBSE Class 10 Maths 1 Mark Questions 1 to 2 ▶
2. Section A | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 1 Mark Question 3 to 4 ▶
3. Section A | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 1 Mark Question 5 to 6 ▶
4. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 7 | Real Numbers ▶
5. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 8 | Arithmetic Progressions ▶
6. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 9 | Coordinate Geometry ▶
7. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 10 | Probability ▶
8. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 11 | Probability ▶
9. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 12 | Linear Equations ▶
10. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 13 | Real Numbers & HCF ▶
11. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 14 | Polynomials ▶
12. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 15 | Linear Equations ▶
13. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 16 | Coordinate Geometry ▶
14. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 17 | Trigonometric Ratios ▶
15. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 18 | Circles ▶
16. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 19 | Triangles ▶
17. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 20 | Areas Related to Circles ▶
18. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 21 | Statistics - Median ▶
19. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 22 | Statistics ▶
20. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 23 | Quadratic Equations ▶
21. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 24 | Arithmetic Progressions ▶
22. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 25 | Triangles ▶
23. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 27 | Trigonometry ▶
24. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 28 | Statistics ▶
25. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 29 | Surface Areas ▶
26. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 30 | Trigonometry ▶
Copyrights © 2016 - 22 All Rights Reserved by Maxtute.com - An Ascent Education Initiative.
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
Mobile: (91) 93822 48484
WhatsApp: WhatsApp Now
Email: [email protected]


 Step 1: In triangle ABE, find tan of angle of elevation and express BE in terms of height of the cloud.
Step 1: In triangle ABE, find tan of angle of elevation and express BE in terms of height of the cloud.