Class 10 Maths Sample Question Paper | 2019
3 Mark Questions | Section C
Section C contains 10 questions of 3 marks each. Scroll down for explanatory answer and video solution to all ten 3-mark questions.The questions appeared from the following topics: Real Numbers, Polynomials, Coordinate Geometry, Linear Equations, Quadratic Equations, Triangles, Circles, Trigonometric ratios, Surface Areas & Volumes, and Statistics.
Question 13
Use Euclid's division algorithm to find the HCF of 726 and 275.
Approach to Find HCF using Euclid's Division Lemma
Step 1: Apply Euclid's Lemma to 726 with 275 as divisor.
Step 2: If a remainder exists, apply the Lemma to the divisor of the preceding step (in this case 275) with remainder of the division of preceding step as the divisor.
Step 3: Continue step 2 till the remainder obtained is 0.
Step 4: The divisor of the last step is the HCF.
Question 14
Find the zeroes of the following polynomial: 5√5 x2 + 30x + 8√5
Approach to solve this Polynomials problem
Factorize the given quadratic polynomial by splitting the middle term.
The product is 200 and the sum is 30. So, the middle term splits as 20x and 30x.
Question 15
Places A and B are 80 km apart from each other on a highway. A car starts from A and another from B at the same time. If they move in same direction they meet in 8 hours and if they move towards each other they meet in 1 hour 20 minutes. Find the speed of cars.
Hint to solve this Linear Equations Word Problem
Step 1: Let the speeds of cars A and B be x and y km/hr respectively.
Step 2: When they travel for 8 hours, A will cover 8x km and B will cover 8y km.
Step 3: Frame equation (1). When they travel in the same direction, the distance covered by A is 80 more than the distance covered by B. So, the difference in distance traveled (8x - 8y) is 80 km.
Step 4: Frame equation (2) similarly when they travel in opposite direction.
Step 5: Solve equations (1) and (2) to find the speeds of the cars.
Question 16 | Internal Choice A
The points A(1, -2) , B(2, 3), C(k, 2) and D(-4, -3) are the vertices of a parallelogram. Find the value of k.
Hint to solve this Coordinate Geometry problem
Property: Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. So, the coordinates of the mid points of the two diagonals are the same.
Step 1: Using mid point formula compute mid points of AC and BD
Step 2: Equate the two expressions to find k.
ORQuestion 16 | Internal Choice B
Find the value of k for which the points (3k-1, k-2), (k, k-7) and (k-1, -k-2) are collinear.
Approach to solve this Coordinate Geometry problem
Step 1: Compute the area of the triangle with the above 3 points as the coordinates of the vertices.
Step 2: Because the 3 points are collinear, the area of the triangle thus formed is 0.
Step 3: Solve the equation to find k.
Question 17 | Internal Choice A
Prove that cot θ – tan θ = \\frac{\text{2 cos^2 θ – 1}}{\text{sin θ cos θ}})
Hint to solve this Trigonometry problem
Step 1: Express LHS in terms of sin θ and cos θ.
Step 2: Take LCM of the resulting expression and apply trigonometric identity Sin2 θ + Cos2 θ = 1 in the numerator to arrive at the RHS.ORQuestion 17 | Internal Choice B
Prove that sin θ(1 + tan θ) + cos θ(1 + cot θ) = sec θ + cosec θ
Hint to solve this Trigonometry problem
Step 1: Express tan θ and cot θ in the LHS in terms of sin θ and cos θ.
Step 2: Simplify the expression to get RHS.
Question 18
The radii of two concentric circles are 13 cm and 8 cm. AB is a diameter of the bigger circle and BD is a tangent to the smaller circle touching it at D and intersecting the larger circle at P on producing. Find the length of AP.
Hint to solve this Circles problem
Step 1: Establish similarity between Δ ABP and Δ OBD by AA similarity.
Step 2: Therefore, AB/OB = AP/OD.
Step 3: Substitute values of AB (diameter of larger circle), OB (radius of larger circle), and OD (radius of inner circle) to find AP
Question 19 | Internal Choice A
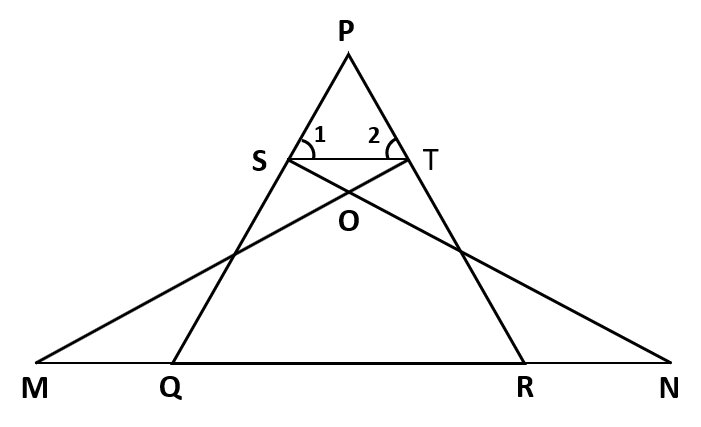
In figure ∠1 = ∠2 and ΔNSQ =≈ Δ MTR, then prove that ΔPTS ~ ΔPRQ.
![2019 SQP CBSE Class 10 Q19A Triangle]()
Hint to solve this Triangles problem
Step 1: Because ∠1 = ∠2, in Δ PTS, sides opposite to the angles PT and PS will be equal.
Step 2: Because ΔNSQ ⩰ ΔMTR, by CPCT ∠NQS = ∠MRT.
Step 3: But ∠NQS = ∠PQR and ∠MRT = ∠PRQ; so, ∠PQR = ∠PRQ.
Step 4: ∴ in Δ PQR, sides opposite to the two angles will be equal. i.e., PR = PQ
Step 5: Because PT = PS and PR = PQ, and ∠ P is common to both triangles Δ PTS and PQR, by SAS the two triangles are similar.
ORQuestion 19 | Internal Choice B
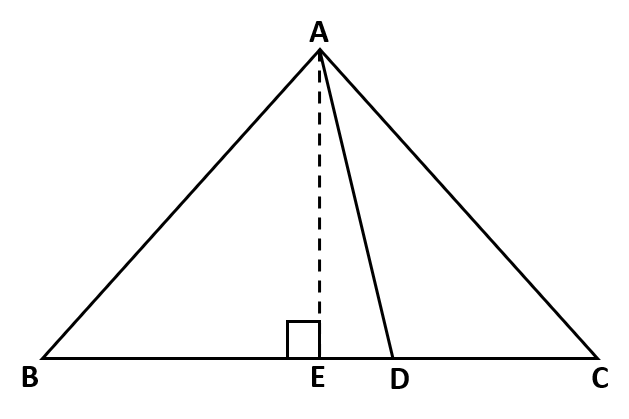
In ΔABC, if AD is the median, then show that AB2 + AC2 = 2(AD2 + BD2)
![2019 SQP CBSE Class 10 Q19A Triangle]()
Hint to solve this Triangles problem
Step 1: Draw perpendicular AE to side BC from A.
Step 2: Apply Pythagoras theorem on two right triangles AEB and AEC.
Step 3: Add the two equations representing the two Pythagoras Theorem.
Step 4: LHS of the addition is the LHS of what is to be proved. Rewrite AE, BE, and CE in terms of AD, ED, BD, ED, and CD, ED to get the RHS.
Question 20
Find the area of the minor segment of a circle of radius 42 cm, if length of the corresponding arc is 44 cm.
Hint to solve this Areas Related to Circles problem
Step 1: Using length of arc and radius of circle, compute ∠AOB, the angle subtended by the sector at the center of the circle.
Step 2: Compute area of sector OADB.
Step 3: Compute area of equilateral triangle AOB.
Step 4: Compute are of minor segment ADB.
Question 21 | Internal Choice A
Water is flowing at the rate of 15 km per hour through a pipe of diameter 14 cm into a rectangular tank which is 50 m long and 44 m wide. Find the time in which the level of water in the tank will rise by 21 cm.
Hint to solve this Surface Areas and Volumes problem
Step 1: Convert all units to metres for uniformity.
Step 2: Compute volume of water flowing through the pipe in 1 hour using information about rate of flow of water through pipe and radius of pipe.
Step 3: Compute volume of water added to the tank when its level rises by 21 cm.
Step 4: Time taken = \\frac{\text{Volume of water added to taken}}{\text{volume flowing through pipe in 1 hour}})
ORQuestion 21 | Internal Choice B
A solid sphere of radius 3 cm is melted and then recast into small spherical balls each of diameter 0.6 cm. Find the number of balls.
Steps to solve this Surface Areas and Volumes problem
Step 1: Number of balls = \\frac{\text{Volume of solid sphere}}{\text{Volume of 1 spherical ball}})
Step 2: Compute volume of solid sphere. Radius = 3 cm.
Step 3: Compute volume of each spherical ball. Raidus = 0.3 cm.
Step 4: Substitute values from steps 2 and 3 in step 1 to find answer.
Question 22
The table shows the daily expenditure on grocery of 25 households in a locality. Find the modal daily expenditure on grocery by a suitable method.
Daily Expenditure 100-150 150-200 200-250 250-300 300-350 Frequency 4 5 12 2 2 Steps to solve this Statistics Question
Step 1: Identify modal class. Highest frequency is 12. So, modal class is 200 - 250.
Step 2: Formula to compute Mode of grouped data = l + [ \\frac{f_1 – f_0}{2f_1 – f_0 − f_2}\\) ] × h
Where l is the lower limit of the modal class & h is the size of the class, f1 is the frequency of the modal class, f0 is the frequency of the preceding class, f2 is the frequency of the succeeding class.
Try CBSE Online Coaching
Class 10 Maths
Register in 2 easy steps and
Start learning in 5 minutes!
FREE Online Revision Classes
CBSE Class 10 Maths - 2021
- Real Numbers Revision Class
- Polynomials Revision Videos
- Linear Equations Revision Class
- Quadratic Equations Revision Class
- Arithmetic Progressions Revision Video
- Triangles Revision
- Coordinate Geometry Revision
- Trigonometry Revision Class
- Appl of Trigonometry
- Circles Revision Class
- Areas Related to Circles Revision Videos
CBSE Online Coaching | Sample Question Paper Class 10 Maths 2019 Video Solution
1. Section A | 2018 CBSE Class 10 Maths 1 Mark Questions 1 to 2 ▶
2. Section A | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 1 Mark Question 3 to 4 ▶
3. Section A | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 1 Mark Question 5 to 6 ▶
4. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 7 | Real Numbers ▶
5. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 8 | Arithmetic Progressions ▶
6. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 9 | Coordinate Geometry ▶
7. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 2 Mark Question 10 | Probability ▶
8. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 11 | Probability ▶
9. Section B | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 12 | Linear Equations ▶
10. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 13 | Real Numbers & HCF ▶
11. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 14 | Polynomials ▶
12. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 15 | Linear Equations ▶
13. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 16 | Coordinate Geometry ▶
14. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 17 | Trigonometric Ratios ▶
15. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 18 | Circles ▶
16. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 19 | Triangles ▶
17. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 20 | Areas Related to Circles ▶
18. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 21 | Statistics - Median ▶
19. Section C | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 3 Mark Question 22 | Statistics ▶
20. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 23 | Quadratic Equations ▶
21. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 24 | Arithmetic Progressions ▶
22. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 25 | Triangles ▶
23. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 27 | Trigonometry ▶
24. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 28 | Statistics ▶
25. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 29 | Surface Areas ▶
26. Section D | 2019 CBSE Class 10 Maths 4 Mark Question 30 | Trigonometry ▶
Copyrights © 2016 - 22 All Rights Reserved by Maxtute.com - An Ascent Education Initiative.
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
Mobile: (91) 93822 48484
WhatsApp: WhatsApp Now
Email: [email protected]