Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 #4
Trigonometry | Trigonometric Values of Complementary Angles
This CBSE class 10 Maths practice question is from the topic Trigonometry. It tests the concept of trigonometric values of complementary angles.
Question 4 : In ΔABC right angled at B, sin C = \\frac{\text{5}}{\text{13}}). Find
(i) sin A
(ii) cos A
(iii) cos C
Target Centum in CBSE 10th Maths
Online CBSE Course
online.maxtute.com
Video Explanation
NCERT Solution to Class 10 Maths
With Videos
Explanatory Answer | Trigonometry Extra Question 4
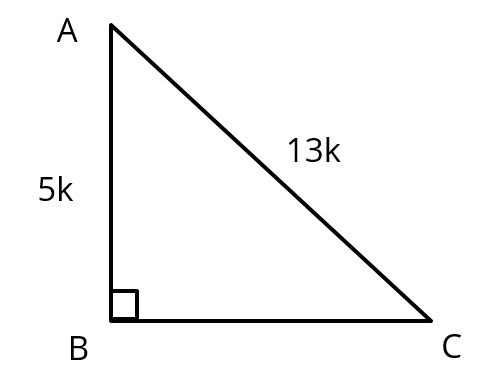
sin C = \\frac{\text{side opposite to ∠C}}{\text{hypotenuse}})=\\frac{\text{AB}}{\text{AC}})= \\frac{\text{5}}{\text{13}}) ...... (1)
Let AB = 5k and AC = 13k
Calculate Sine and Cosine values of the angles
Using Pythagoras theorem, BC = \\sqrt{AC^2− AB^2});
BC = \\sqrt{(13k)^2− (5k)^2 }) = \\sqrt{169 k^2− 25 k^2 }) = \\sqrt{144k^2 }) = 12k
sin A = \\frac{\text{side opposite to ∠A}}{\text{hypotenuse}})= \\frac{\text{BC}}{\text{AC}})= \\frac{\text{12k}}{\text{13k}})= \\frac{\text{12}}{\text{13}}) ...... (2)
cos A = \\frac{\text{side adjcent to ∠ A}}{\text{hypotenuse}}) = \\frac{\text{AB}}{\text{AC}})= \\frac{\text{5k}}{\text{13k}})= \\frac{\text{5}}{\text{13}}) ...... (3)
cos C = \\frac{\text{side adjcent to ∠ C}}{\text{hypotenuse}})= \\frac{\text{BC}}{\text{AC}}) = \\frac{\text{12k}}{\text{13k}}) = \\frac{\text{12}}{\text{13}}) ...... (4)
Inference
From (1) and (3): sin A = cos C
From (2) and (4): sin C = cos A
Why?
If ABC is right angled at B, side adjacent to ∠ A will be the side opposite to ∠C.
Similarly side opposite to ∠A will be the side adjacent to ∠C.
i.e., ∠A = 90° - ∠C and ∠C = 90° - ∠A
Try CBSE Online Coaching
Class 10 Maths
Register in 2 easy steps and
Start learning in 5 minutes!
FREE Online Revision Classes
CBSE Class 10 Maths - 2021
- Real Numbers Revision Class
- Polynomials Revision Videos
- Linear Equations Revision Class
- Quadratic Equations Revision Class
- Arithmetic Progressions Revision Video
- Triangles Revision
- Coordinate Geometry Revision
- Trigonometry Revision Class
- Appl of Trigonometry
- Circles Revision Class
- Areas Related to Circles Revision Videos
CBSE Online Coaching | Class 10 Maths - Trigonometry Extra Practice Questions
1. Trigonometric Ratios | CBSE Class 10 Extra Practice Question #01 | Easy Question Questions 1 ▶
2. Trigonometric Ratios | CBSE Class 10 Math Additional Practice Question #02 | Easy Question Question 2 ▶
3. Trigonometric values | CBSE Class 10 Math Extra Question #03 | Medium Question Question 3 ▶
4. Trigonometry theory & practice | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #04 | Medium Question Question 4 ▶
5. Trigonometric Ratios | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #05 | Easy Question Question 5 ▶
6. Trigonometry & Quadratic Equation | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #06 | Medium Question Question 6 ▶
7. Trigonometric values| CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #07 | Easy Question Question 7 ▶
8. Trigonometric Ratios | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #08 | Easy Question Question 8 ▶
9. Trigonometric values | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #09 | Easy Question Question 9 ▶
10. Trigonometric values | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #10 | Easy Question Question 10 ▶
11. Square of Trigonometric Ratios | CBSE Class 10 Extra Question #11 | Easy Question Question 11 ▶
12. Trigonometric values | CBSE 10th Extra Practice Question #12 | Easy questions Question 12 ▶
13. Trigonometric Values of Basic Angles | CBSE 10th Extra Question #13 | Easy question Question 13 ▶
14. Trigonometric Ratios of Specific Values | CBSE Class 10 Important Question #14 | Hard Question Question 14 ▶
15. Trigonometric Ratio & Linear Equations | CBSE Class 10 Important Question #15 | Hard Question Question 15 ▶
Copyrights © 2016 - 22 All Rights Reserved by Maxtute.com - An Ascent Education Initiative.
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
Mobile: (91) 93822 48484
WhatsApp: WhatsApp Now
Email: [email protected]
