Question In the given figure, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C, is intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90°.
Video Explanation
Explanatory Answer
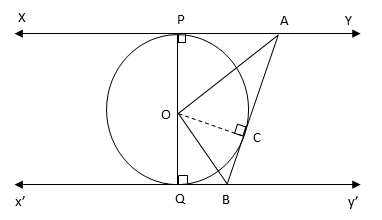
Because the radius and tanget meet at right angles at the point of tangency, ∠OPA = 90°; ∠OQB = 90° and ∠OCA = 90°
AP and AC are equal tangents from A. OP and OC are equal as they are radii to the circle. And OA is a side common to triangles OPA and OCA.
By SSS rule ΔOPA \\equiv ) ΔOCA (Trianlges OPA and OCA are congruent)
Therefore, ∠PAO = ∠CAO. Let it be ‘x’.
And ∠AOP = ∠AOC. Let it be ‘a’.
BQ and BC are equal tangents from an external point B.
OQ and OC are radii and are equal.
OB is a side common to OQB and OCB.
By SSS rule ΔOQB \\equiv ) ΔOCB (Trianlges OQB and OCB are congruent)
Therefore, ∠OBQ = ∠OBC. Let it be ‘y’.
And ∠QOB = ∠COB. Let it be ‘b’.
∠AOB = ∠AOC + ∠COB = a + b
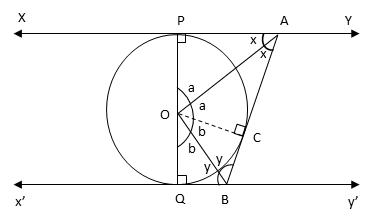
In Δ OPA, x + a + 90° = 180°
Or a = 90° - x
Similarly in ΔOCB, y + b + 90° = 180°
Or b = 90° - y
Therefore, ∠AOB = a + b = (90 – x) + (90 – y) = 180 – (x + y)
Lines xy and x’y’ are parallel
Therefore, ∠CBy’ = 2x (Alternate interior angles are equal)
Because x’y’ is a straight line, ∠QBC + ∠CBy’ = 180°
I.e., 2y + 2x = 180°
Or x + y = 90°
Therefore, ∠AOB = 180 – (x + y) = 180 – 90 = 90°
.